Junit
简介
官网https://junit.org/junit4/
导入
- 创建一个普通Maven项目
- 在pom.xml中引入依赖
Maven
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
|
注:junit4.11以上版本不在包含hamcrest,需要手动安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hamcrest/hamcrest-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
|
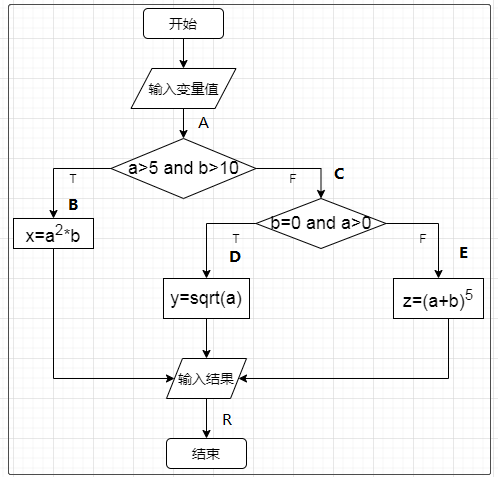
覆盖测试

对应代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public double getData(int a, int b) {
double x = 0, y = 0, z = 0;
if (a > 5 && b > 10) {
x = Math.pow(a, 2) * b;
return x;
} else {
if (b == 0 && a > 0) {
y = Math.sqrt(a);
return y;
} else {
z = Math.pow(a + b, 5);
return z;
}
}
}
|
条件覆盖
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(getData(6, 12)); //R==>6^2*12=432 A-B
System.out.println(getData(1,2)); // R==>(3+2)^5=243.0 A-C-D
System.out.println(getData(4,0)); // R==>sqrt(4)= 2 A-C-E
}
|
断言
常用匹配方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//要求所有的条件都要通过测试才算成功
assertThat("hello world", allOf(startsWith("helloo"), containsString("world"))); //false
//如果接下来的所有条件只要有一个成立则测试通过
assertThat("hello world", anyOf(startsWith("hello"), containsString("worldd"))); //true
//anything匹配符表明无论什么条件,永远为true
assertThat( "hello world", is( "hello" ) ); //true
//is表明如果前面待测的object等于后面给出的object
assertThat( "hello world", is( "hello world") ); //true
//not匹配符和is匹配符正好相反,表明如果前面待测的object不等于后面给出的object
assertThat( "hello world", not( "hello world") ); //false
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//判断是否包含字符串
assertThat( "helloWorld", containsString( "hello" ) ); //true
//判断是否以指定字符串结尾
assertThat( "helloWorld", endsWith( "World" ) ); //true
//判断是否以指定字符串开始
assertThat( "helloWorld", startsWith( "hello" ) ); //true
//equalTo匹配符表明如果测试的testedValue等于expectedValue则测试通过
assertThat( "hello", equalTo("hello") );
//判断忽略首尾空格时是否相等
assertThat( "hello", equalToIgnoringWhiteSpace( " hello " ) ); //true
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//判断列表中是否包含指定项
assertThat(Arrays.asList("foo", "bar"), hasItem("bar"));
//判断列表中是否包含多项
assertThat(Arrays.asList("foo", "bar", "baz"), hasItems("baz", "foo"))
//判断指定对象是否是某个类(包括子类)
assertThat(new ArrayList<>(), instanceOf(List.class));
|
注意事项:
要注意区分error和failure!!!
failure是指:被测程序的逻辑有错误,得不到预期的值。执行了junit的断言。
error是指:被测程序本身抛出的异常,还没有执行到junit的断言就抛出了异常。
Junit测试类注解
| junit4 |
junit5 |
特点 |
| @BeforeClass |
@BeforeAll |
在当前类的所有测试方法之前执行。注解在【静态方法】上。 |
| @AfterClass |
@AfterAll |
在当前类中的所有测试方法之后执行。注解在【静态方法】上。 |
| @Before |
@BeforeEach |
在每个测试方法之前执行。注解在【非静态方法】上。 |
| @After |
@AfterEach |
在每个测试方法之后执行。注解在【非静态方法】上。 |
区别:
- @AfterClass修饰public static void 、@After修饰public void
- @AfterClass在一个测试类中只能一个,但是@After可以有多个
- @AfterClass只执行一次,是在所有@Test方法执行完成后、@After在每个@Test方法执行完成后都会执行
@RunnerTest测试运行器
Junit测试套件
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class JunitTestOne {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("测试一。。。");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class JunitTestTwo {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("测试二。。。");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class JunitTestThree {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("测试三。。。");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@RunWith(Suite.class)
@Suite.SuiteClasses({ JunitTestOne.class,JunitTestTwo.class ,JunitTestThree.class})
public class AllTests {
}
|
此时执行Alltests会同时执行三个测试方法
Junit异常测试
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Test(expected = IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void test (){
List<String> lists = new ArrayList<>();
lists.get(1);
}
|
@expected表达式表示如果方法抛出指定异常则测试通过,以上例子可以通过测试。
Junit限时测试
例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Test(timeout = 1000)
public void test (){
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
@timeout表达式表示如果方法运行市场超过指定行数则测试不通过,以上案例中使用线程阻塞的方式阻塞线程2000毫秒,超过了规定时间,所以测试不通过。
Junit参数化测试
步骤:
-
编写参数化测试类并标注 @RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
-
定义公共变量用于设置参数(用例参数,预期值)
-
编写全参构造方法用于传值
-
编写一个返回集合的静态类用于传入测试用例值 并标注@Parameters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
@RunWith(value = Parameterized.class)
public class ParameterizedTest {
private int a;
private int b;
private double expected;
// Inject via constructor
// for {8, 2, 10}, numberA = 8, numberB = 2, expected = 10
public ParameterizedTest(int numberA, int numberB, double expected) {
this.a = numberA;
this.b = numberB;
this.expected = expected;
}
// name attribute is optional, provide an unique name for test
// multiple parameters, uses Collection<Object[]>
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{6, 12, 432.0},
{1, 2, 243.0},
{4, 0, 2.0},
});
}
@Test
public void test_getData() {
TestCode testCode = new TestCode();
assertThat(testCode.getData(a, b), equalTo(expected));
}
}
|
Junit优先级测试
参数:MethodSorters.JVM(按照JVM得到的顺序执行)
MethodSorters.NAME_ASCENDING(按照名字顺序)